Overview
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by the narrowing of the lung’s airways and an increase in mucus production, resulting in breathing difficulties and coughing. The severity of asthma can vary among individuals, and it can affect people of all ages.
While there is no known cure for asthma, the primary approach to managing the condition is through symptomatic treatment, focusing on alleviating symptoms and improving quality of life.
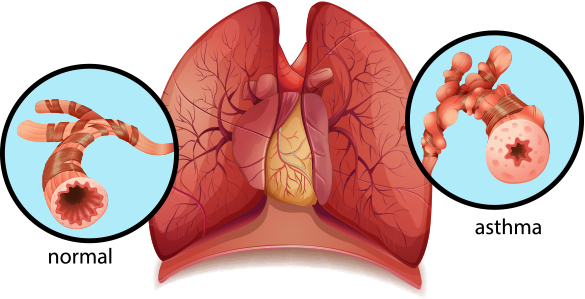
Symptoms of Asthma
Following are some of the common symptoms of asthma:
- Wheezing
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing
- Chest tightness
- Fatigue
- Difficulty sleeping
- Rapid breathing
- Increased mucus production
Above mentioned symptoms can sometimes get worse and cause a condition known as asthma attack.
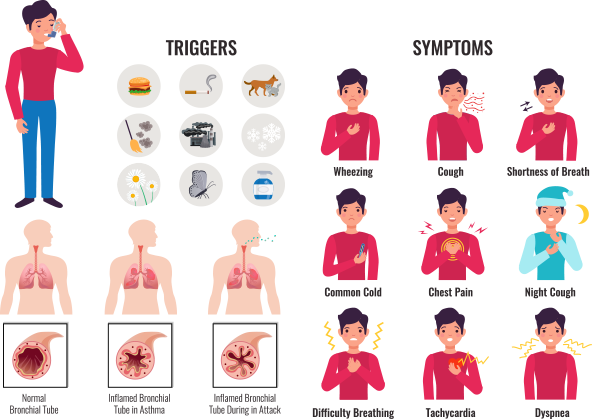
Causes and Triggers of Asthma
Some of the common causes and triggers of asthma are:
- Allergens such as pollens, dust mites, pet dander, mold spores and certain foods. These can irritate the airways and causes asthmatic symptoms.
- Respiratory infections such as common cold, flu and sinusitis.
- irritants and pollutants such as smoke, pollution, strong odors, chemical fumes etc.
- Exercise and physical activity.
- Emotional stress and intense emotions such as anxiety and or laughter.
- Weather conditions such as cold air, humidity or any change in barometric pressure.
Treatment of Asthma
Treatment of asthma targets mainly to control and manage the symptoms. This helps to reduce inflammation in the airways leading to reduction in the asthmatic attacks. The specific treatment plan for asthma may vary depending on the severity of the condition.

1. Inhaled Corticosteroids
They help to prevent swelling of airways, which leads to the reduction in mucus production. These medications are taken via a device called as an inhaler, it helps to get the medicine into your lungs. These include:
- Beclomethasone
- Budesonide
- Fluticasone
2. Leukotriene Modifiers
These are another class of medications targeted to eat long term asthmatic symptoms. Leukotrienes trigger an asthma attack in your body, these modifiers blocks them. Medications include but not limited to:
- Montelukast
- Zafirlukast
3. Long Acting Beta Agonists (LABA)
LABA are also called as bronchodilators. They relax the muscles surrounding the airways of the lungs. LABA are taken via an inhaler. Medications include but not limited to:
- Ciclesonide
- Formoterol
- Mometasone
- Salmeterol
4. Combination Inhaler
It is a combination of Corticosteroid and long acting beta agonist (LABA), to ease asthmatic symptoms. Medications include but not limited to:
- Budesonide and Formoterol
- Fluticasone and Salmeterol
- Fluticasone and Vilanterol
- Mometasone and Formoterol
5. Theophylline
It is also used for the ease of long term asthmatic symptoms, helps to relax the airways and reduce tightness in your chest. It can be taken by mouth itself or with an inhaled corticosteroid.
6. Short Acting Beta Agonists (SABA)
Also called as rescue inhalers, helps to relax the muscle bands surrounding the airways and ease symptoms. Medications include but not limited to:
- Albuterol
- Levalbuterol
7. Anticholinergics
Another class of bronchodilators, helps to relax the muscles surrounding the airways. These medications are typically administered through inhalers. Medications include but not limited to:
- Ipratropium
- Tiotropium bromide
8. Oral Corticosteroids
Taken along with rescue inhalers during asthma attack. Helps to ease out the swelling and inflammation of the airways. Oral steroids are taken for a short time, between 5 days and 2 weeks usually. Medications include but not limited to:
- Methylprednisolone
- Prednisolone
- Prednisone
What are the Complications of Asthma?
Asthma, if not properly managed, can lead to various complications that can affect the quality of life and overall health of individuals:
- Lack of exercise and weight gain.
- Fatigue
- Sleep disturbances
- Work and school absences
- Emotional and psychological disturbances such as anxiety, stress and depression
- Reduced lung function
- Respiratory infections
- Early delivery or loss of pregnancy
- Lung collapse

How to Prevent an Asthma Attack?
Preventing asthma attacks involves taking proactive measures to minimize triggers and maintain good control of the condition. Here are some strategies to help prevent asthma attacks:
- Take medications as prescribed
- Identify and avoid your triggers
- Create a clean and allergen free environment
- Practice good hygiene
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle by practicing mild physical movements like yoga, walk etc.
- Follow an asthma action plan
- Regularly monitor lung function
- Keep rescue medications handy
- Attend regular checkups
Prevention is better than cure, furthermore, asthma requires active management to reduce the frequency of attacks. By following above mentioned measures, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of experiencing asthma attacks.
How Asthma is Diagnosed?
Asthma is typically diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Here are the key steps involved in the diagnosis of asthma:
1. Medical History
Medical history includes questions regarding your symptoms, their frequency and duration, and triggers. It also include personal and family medical history, along with allergies or respiratory conditions.
2. Physical Examination
It is performed to assess the status of your respiratory system. Your healthcare provider will use a stethoscope to check for wheezing, chest tightness and respiratory distress.
3. Spirometry
It is a lung function test, helps to diagnose and monitor asthma. This test helps to find out if there is any obstruction in the airway and helps to define the functioning of the lungs.
4. Bronchodilator Response Test
This test is usually given after initial spirometry test, a bronchodilator medication is given to inhale, after that, spirometry test is repeated to make sure if there is good improvement in lung function, which suggests reversible airway obstruction commonly seen in asthma.
5. Peak Flow Monitoring
Used to track asthma symptoms and assess response treatment. This is an at home monitoring tool used to measure how fast you can exhale air.
6. Allergy Testing
Blood tests or allergy skin tests helps to identify specific allergens that trigger asthmatic symptoms, helps to develop management plan.
7. Additional Tests
Some of the additional tests include chest X-ray or methacholine challenge test, for confirmation of the presence of asthma or determination of other respiratory conditions.
It’s essential to note that the diagnosis of asthma is typically made based on a combination of clinical evaluation, symptom patterns, and test results. Working closely with a healthcare professional experienced in diagnosing and managing asthma is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
A Word from Prolific Blogs!
The key to managing asthma lies in understanding and controlling the triggers that worsen symptoms. This involves working closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized asthma action plan, which may include medications for long-term control and quick relief during attacks. Regular check-ups, monitoring lung function, and adhering to prescribed medications are vital for keeping asthma under control.
Prevention plays a crucial role in minimizing the risk of asthma attacks. Identifying and avoiding triggers, creating an allergen-free environment, practicing good hygiene, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of symptoms. Education and self-management are also essential, as individuals with asthma should be equipped with knowledge about their condition and how to handle potential flare-ups.